What Is New about BLUE
STAR STING
What Is New about BLUE
STAR STING
 |
The latest version is Blue Star Sting, released in June, 2006 |
New features introduced in Blue Star
Sting:
#
New Feature
Blue Star
Sting/ Star Sting difference
Description
1
3D Java Protein Interface Viewer
- JPIV ®
-
Designed to visualize separately
the protein interfaces and analyze the main forces involved
in protein complex formation.
2
2-Dimensional Interface Maps - 2DIM
-
Designed to visualize separately
the protein interfaces and analyze the main forces involved
in protein complex formation. The 2DIM uses Floater's shape
preserving algorithm to project the 3D protein interfaces into
2D, where it is then possible to superimpose the surfaces and
estimate the interaction area between them.
3
Sting Enzyme Classification ®
-
Module dealing with a protein classification
based on STING_DB parameters.
4
PL Contacts ®
-
This STING module can analyze the interatomics
contacts in protein-ligand complexes. The contacts shown by
this STING module include those mediated by charge-charge interactions
hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts.
5
Topologs 100 ®
-
In this module, users can obtain
the index for a toplogy similarity for a list of up to 100 structures.
By submitting the STING TGZ file (containing all STING_DB parameters,
precalcualated, corresponding to certain public or local structure)
and a text file containing the list of up to 99 public PDB files,
user can start the procedure which calculates the similarity
index among selected (up to) 100 structures. This index is a
reliable measure of the changes in the pattern of the intrachain
interactions and can be used to analyse the topology similarities.
6
Topologs Astral 40®
-
This is a database of homologous PDB chains based
on their interactions (contacts) pattern. For each of the "ASTRAL
40" ensamble chains, we computed a list of the most similar
chains based on their contact maps. The database is searchable
and for each chain, the list of the topologs is presented.
7
AA Co-evolution ®
-
The "AA Co-evolution"
is the STING component which permits a user to examine co-evolution
parameter of residues in a simples, yet intuitive, 3D plot.
A user might confirm which amino-acid positions were identified
by STING, within the previously confirmed amino acid conserved
set, as evolved in concert.
8
STING Report ®
-
The STING Report module has been expanded with
the new parameters and module images.
9
Multiple Parameter Aligment
3D Plot ®
-
Deal with the presentation
of a single parameter for multiple structures or multiple parameters
for a singles structure.
10
Java instead of GD Perl library for image generation
-
STAR Sting
was released in February 14, 2006
[ reference
]
New features introduced in Star Sting:
#
New Feature
Star Sting/
Diamond Sting difference
Description
1
Multiple Structure - Single Parameter (MSSP)
2D Plot ®
-
Multiple Structure - Single Parameter (MSSP)
2D plot is designed for comparing a chosen parameter among several
structures.
2
Contact Distance Map ®
-
Contact Distance Map (CDM) module is designed for simultaneous
visualization of the 5 classes of contacts for all amino acids
of a chosen structure.
3
Protein Contacts Difference®
-
In STING_PCD users can obtain
a complete comparison report of the intrachain interactions for
any two chains described in the PDB format file. The user must
supply any two PDB ids and corresponding chain ids for the analysis.
At the output, a user will receive a list of interactions which
were preserved in both chains as well as the list of those which
are present in only one of them. Users can also analyse a wild
type protein and a corresponding mutant structure with a single
point mutantion; in this case a user needs to supply at the input,
the mutated amino acid name and the number.
4
Topology Similarity Map (TopSiMap) ®
-
STING_TopSiMap is a module which makes possible
to compare the contact maps of two chains in terms of the preserved
interactions as well as the ones which are present in only one
of the two chains analysed. Users can see / print the images of
the maps and also view the contacts in a JMol window where STING
presents two structurally aligned chains. Users can also compare
the chains in terms of the contacts classification (hydrophobic,
aromatic stacking, hydrogen bonds, salt bridges and cysteine bridges)
and corresponding energies.
5
STING_DB QA®
-
This module is designed for checking the quality
of STING_DB, the STING_DB Quality Assessment (STING_DB QA). With
this new module, a user can perform the tracking of the PDB files
which contains the insufficient information clarity for a specific
structure descriptor calculation. Also, the overall quality of
the STING_DB is much easier to assess now, setting this STING
version apart from other products in this area.
6
STING_TGZ®
-
Using STING_TGZ module, the production of "TGZ"
files, containing all STING_DB parameters is now possible for
up to 5 public PDB files.
7
Improved select feature
-
In Star STING we improved the
procedure for selecting the structure parameter ranges while searching
for those amino acids that satisfy particular conditions. Most
importantly, the parameter ranges could now be saved and transferred
from one STING session to the other, greatly facilitating the
process of selction. In addition, a user is now able to make the
choice of the range using either the keyboard (entering the numerical
values) or the sliding button on the range scale of the SELECT
window.
8
STING Report ®
-
The STING Report module has been expanded with
the new parameters and module images.
9
JMOL/Chime
-
By introducing of a dual graphical
viewer capability to Star STING, with the option for either Jmol
or Chime we made possible the use of STING across the major platforms
and browsers (due to a fact that JMOL is operational on all those
platforms and browsers).
10
Contacts improvement
-
The two STING_DB per-residue-reported structure
descriptors: the Order of Cross Link and Order of Cross Presence,
are re-calculated, using new default input parameter settings
for the corresponding programs which calculate those structure
descriptors. In this case we have introduced a more restrictive
conditions for counting in any residue as having a higher order
cross link. This is done by introduction of additional requirement
that the target AA also must be at least 15 residues appart in
the primary sequence.
11
Evolutionary pressure database
recalculated for new rate4site
-
This particular STING_DB per-residue-reported
structure descriptor: Evolutionary Pressure is re-calculated,
using new default input parameter settings for the corresponding
programs which calculate those structure descriptor.
12
Introduction of the third STING window - general
information on PDB file and corresponding structure
-
On the opening of STING, a user is now presented
with a third window: "At-a-glance", offering general
information on this specific PDB entry, facilitating analysis
by displaying some background information and summaries.
| New features introduced in Blue Star Sting: |
| # |
New Feature |
Blue Star
Sting/ Star Sting difference |
Description |
| 1 | 3D Java Protein Interface Viewer - JPIV ® | - |
Designed to visualize separately the protein interfaces and analyze the main forces involved in protein complex formation. |
| 2 | 2-Dimensional Interface Maps - 2DIM | - |
Designed to visualize separately the protein interfaces and analyze the main forces involved in protein complex formation. The 2DIM uses Floater's shape preserving algorithm to project the 3D protein interfaces into 2D, where it is then possible to superimpose the surfaces and estimate the interaction area between them. |
| 3 | Sting Enzyme Classification ® | - |
Module dealing with a protein classification based on STING_DB parameters. |
| 4 | PL Contacts ® | - |
This STING module can analyze the interatomics contacts in protein-ligand complexes. The contacts shown by this STING module include those mediated by charge-charge interactions hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts. |
| 5 | Topologs 100 ® |
- |
In this module, users can obtain the index for a toplogy similarity for a list of up to 100 structures. By submitting the STING TGZ file (containing all STING_DB parameters, precalcualated, corresponding to certain public or local structure) and a text file containing the list of up to 99 public PDB files, user can start the procedure which calculates the similarity index among selected (up to) 100 structures. This index is a reliable measure of the changes in the pattern of the intrachain interactions and can be used to analyse the topology similarities. |
| 6 | Topologs Astral 40® | - |
This is a database of homologous PDB chains based on their interactions (contacts) pattern. For each of the "ASTRAL 40" ensamble chains, we computed a list of the most similar chains based on their contact maps. The database is searchable and for each chain, the list of the topologs is presented. |
| 7 | AA Co-evolution ® |
- |
The "AA Co-evolution" is the STING component which permits a user to examine co-evolution parameter of residues in a simples, yet intuitive, 3D plot. A user might confirm which amino-acid positions were identified by STING, within the previously confirmed amino acid conserved set, as evolved in concert. |
| 8 | STING Report ® | - |
The STING Report module has been expanded with the new parameters and module images. |
| 9 | Multiple Parameter Aligment 3D Plot ® |
- |
Deal with the presentation of a single parameter for multiple structures or multiple parameters for a singles structure. |
| 10 | Java instead of GD Perl library for image generation |
- |
STAR Sting
was released in February 14, 2006
[ reference
]
|
New features introduced in Star Sting: |
| # |
New Feature |
Star Sting/
Diamond Sting difference |
Description |
| 1 | Multiple Structure - Single Parameter (MSSP) 2D Plot ® | - |
Multiple Structure - Single Parameter (MSSP) 2D plot is designed for comparing a chosen parameter among several structures. |
| 2 | Contact Distance Map ® | - |
Contact Distance Map (CDM) module is designed for simultaneous visualization of the 5 classes of contacts for all amino acids of a chosen structure. |
| 3 | Protein Contacts Difference® | - |
In STING_PCD users can obtain a complete comparison report of the intrachain interactions for any two chains described in the PDB format file. The user must supply any two PDB ids and corresponding chain ids for the analysis. At the output, a user will receive a list of interactions which were preserved in both chains as well as the list of those which are present in only one of them. Users can also analyse a wild type protein and a corresponding mutant structure with a single point mutantion; in this case a user needs to supply at the input, the mutated amino acid name and the number. |
| 4 | Topology Similarity Map (TopSiMap) ® | - |
STING_TopSiMap is a module which makes possible to compare the contact maps of two chains in terms of the preserved interactions as well as the ones which are present in only one of the two chains analysed. Users can see / print the images of the maps and also view the contacts in a JMol window where STING presents two structurally aligned chains. Users can also compare the chains in terms of the contacts classification (hydrophobic, aromatic stacking, hydrogen bonds, salt bridges and cysteine bridges) and corresponding energies. |
| 5 | STING_DB QA® | - |
This module is designed for checking the quality of STING_DB, the STING_DB Quality Assessment (STING_DB QA). With this new module, a user can perform the tracking of the PDB files which contains the insufficient information clarity for a specific structure descriptor calculation. Also, the overall quality of the STING_DB is much easier to assess now, setting this STING version apart from other products in this area. |
| 6 | STING_TGZ® | - |
Using STING_TGZ module, the production of "TGZ" files, containing all STING_DB parameters is now possible for up to 5 public PDB files. |
| 7 | Improved select feature | - |
In Star STING we improved the procedure for selecting the structure parameter ranges while searching for those amino acids that satisfy particular conditions. Most importantly, the parameter ranges could now be saved and transferred from one STING session to the other, greatly facilitating the process of selction. In addition, a user is now able to make the choice of the range using either the keyboard (entering the numerical values) or the sliding button on the range scale of the SELECT window. |
| 8 | STING Report ® | - |
The STING Report module has been expanded with the new parameters and module images. |
| 9 | JMOL/Chime | - |
By introducing of a dual graphical viewer capability to Star STING, with the option for either Jmol or Chime we made possible the use of STING across the major platforms and browsers (due to a fact that JMOL is operational on all those platforms and browsers). |
| 10 | Contacts improvement | - |
The two STING_DB per-residue-reported structure descriptors: the Order of Cross Link and Order of Cross Presence, are re-calculated, using new default input parameter settings for the corresponding programs which calculate those structure descriptors. In this case we have introduced a more restrictive conditions for counting in any residue as having a higher order cross link. This is done by introduction of additional requirement that the target AA also must be at least 15 residues appart in the primary sequence. |
| 11 | Evolutionary pressure database recalculated for new rate4site |
- |
This particular STING_DB per-residue-reported structure descriptor: Evolutionary Pressure is re-calculated, using new default input parameter settings for the corresponding programs which calculate those structure descriptor. |
| 12 | Introduction of the third STING window - general information on PDB file and corresponding structure |
- |
On the opening of STING, a user is now presented with a third window: "At-a-glance", offering general information on this specific PDB entry, facilitating analysis by displaying some background information and summaries. |
DIAMOND Sting
was released in February 14, 2005
[ reference
]
New features introduced in Diamond Sting:
#
New Feature
Diamond Sting/
Gold Sting difference
Description
1
Rotamers ®
-
Side chain torsion angles fall into n-dimensional
clusters. Rare rotamers are defined as those torsion angles that
are not close enough (Euclidean distance greater than a given
limit). This information is now available both in the JPD and
STING Report.
2
Order of Cross Link ®
-
Cross Links are defined as contacts
(any type from possible 5 classes: 1. Hydrophobic interaction,
2. Hydrogen Bonding, 3. Aromatic Stacking, 4. Salt bridging, 5.
Cystein-bridging) established among residues that are far apart
in the protein primary sequence, but are close in its 3D fold.
The order is identified as a number of such cross-links. The higher
the order, the more important that residue must be for the protein
folding/stability.
3
Order of Cross Presence ®
-
Cross Presence is defined as presence within a
probing sphere (centered at a given residue) of any residue that
is far apart in the protein primary sequence from the central
residue, but is close in its 3D fold. The order is identified
as a number of such cross-presence encounters. The higher the
order, the more important that residue must be for the protein
folding/stability. Order of Cross-Presence normally is higher
than the order of Cross Link for any given amino acid, due to
the simple fact the not all Present residues will actually engage
in one of 5 possible contact types.
4
Space Clash ®
-
Space Clash is an important measure
of how well defined is the overall protein structure and in particular
of how are the atoms of amino acid side chains packed. We calculate
Space Clashes and then represent them by classifying the degree
of penetration into the space occupied by the other atom.
5
PDB Metrics ®
-
The Protein Database Metrics or PDB-Metrics is the new implementation
of a discontinued STING module called PDB_Mining. PDB Metrics
provides a summary of the protein structures deposited in the
Protein Data Bank (PDB). It offers a vast collection of descriptors
and means to recover specific PDB files. PDB-Metrics is a powerful
tool for the bioinformatics researcher to analyze the PDB's
collection of protein structure descriptions from a variety
of perspectives, and recover specific files using a repertoire
of alternate criteria.
6
ProTherm ®
-
ProTherm is a thermodynamic database for proteins
and mutants, containing several thermodynamic parameters along
with experimental methods and conditions, and structural, functional
and literature information. The sequence and structural information
of proteins is connected with thermodynamic data through links
between entries in Protein Data Bank, Protein Information Resource
and SWISS-PROT and the data in ProTherm. ProTherm now has a separated
field for the Gibbs free energy change obtained at extrapolated
temperature from the data on denaturation temperature measured
by the thermal denaturation method. Both JPD and STING Report
now offer link to ProTherm specific page and embedded parameter
which indicates how many mutations exist in ProTherm DB for a
given residue in a given PDB structure. In collaboration with
Akinori Sarai's group, we have completely reorganized the table
of indexes for easier identification of ProTherm entries on residue
by residue basis (anchored to the specific PDB entry).
7
Ca/Ca- Cß/Cß
Detailed and Global Insight ®
-
Earlier version of the Ca/Ca-
Cß/Cß Java Plot was not very
practical if a user would like to examine the global plot of the
protein with more than 100 amino acids. Current Diamond STING
version of Ca/Ca- Cß/Cß
Java Plot has both the global and detailed view easily generated
and presented for analysis.
8
Adjustment for Color Range/Intensity in JPD
®
-
Current version of JavaProtein Dossier permits adjustment
of the color range for easier grasping of the differences among
residues. The parameters might be now painted according to the
numerical/color values spanning Min/Max range for the whole PDB,
for the Protein family, for a given PDB structure and for specific
parameter line. Although this feature does not influence the SELECT
process, it does enhance the visual identification of amino acids
having a different parameter value/color from the others within
a same structure.
9
Extended SELECT in JPD
®
-
Current DIAMOND STING SELECT feature
is more powerful than the earlier as we added several enhancement
options for the parameter range selection and Boolean logic combinations
as well as by adding the new parameters to be selected from.
10
Local File by e-mail ®
-
One of the main new features added to DIAMOND STING
is the ability of the STING server to handle a user request for
calculating all structure parameters for nonpublic (non PDB deposited)
structure - a local file. As such requests are numerous and are
CPU time demanding, it was very important to introduce a control
of CPU use by placing all request in a job request list, executed
by the order of arrival by 4 dedicated CPUs.
11
Sting Report Expanded and now available for
a Whole Protein Chain Descriptors
®
-
Main addition in STING Report is that the DIAMOND version now
contains all new parameters (Order of CrossLink, Order of CrossPresence,
Space Clash, Rotamer Library ID, ProTherm ID) in addition to
the chain descriptors:
1. Total volume of the chain
2. Total surface area of the chain
3. Ratio of volume to surface
4. Ratio of total surface to surface at interface
5. Density for entire chain
6. Sponge for entire chain
7. Total number of
a) H-bonds
b) salt bridges
c) hydrophobic interactions
d) cystein bridges
e) aromatic stacking
interactions.
8. Consequently: total energy of established contacts for the
chain
9. Energy of the contacts divided by the volume
10. Average Relative Entropy (not sure about this!?)
11. Total surface area occupied by hot spots
12. Hot spot area divided by total surface area of molecule
13. Total pocket surface area
14. Total pocket volume area
15. Total cavity volume
|
New features introduced in Diamond Sting: |
| # |
New Feature |
Diamond Sting/
Gold Sting difference |
Description |
| 1 | Rotamers ® | - |
Side chain torsion angles fall into n-dimensional clusters. Rare rotamers are defined as those torsion angles that are not close enough (Euclidean distance greater than a given limit). This information is now available both in the JPD and STING Report. |
| 2 | Order of Cross Link ® | - |
Cross Links are defined as contacts (any type from possible 5 classes: 1. Hydrophobic interaction, 2. Hydrogen Bonding, 3. Aromatic Stacking, 4. Salt bridging, 5. Cystein-bridging) established among residues that are far apart in the protein primary sequence, but are close in its 3D fold. The order is identified as a number of such cross-links. The higher the order, the more important that residue must be for the protein folding/stability. |
| 3 | Order of Cross Presence ® | - |
Cross Presence is defined as presence within a probing sphere (centered at a given residue) of any residue that is far apart in the protein primary sequence from the central residue, but is close in its 3D fold. The order is identified as a number of such cross-presence encounters. The higher the order, the more important that residue must be for the protein folding/stability. Order of Cross-Presence normally is higher than the order of Cross Link for any given amino acid, due to the simple fact the not all Present residues will actually engage in one of 5 possible contact types. |
| 4 | Space Clash ® | - |
Space Clash is an important measure of how well defined is the overall protein structure and in particular of how are the atoms of amino acid side chains packed. We calculate Space Clashes and then represent them by classifying the degree of penetration into the space occupied by the other atom. |
| 5 | PDB Metrics ® | - |
The Protein Database Metrics or PDB-Metrics is the new implementation of a discontinued STING module called PDB_Mining. PDB Metrics provides a summary of the protein structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB). It offers a vast collection of descriptors and means to recover specific PDB files. PDB-Metrics is a powerful tool for the bioinformatics researcher to analyze the PDB's collection of protein structure descriptions from a variety of perspectives, and recover specific files using a repertoire of alternate criteria. |
| 6 | ProTherm ® |
- |
ProTherm is a thermodynamic database for proteins and mutants, containing several thermodynamic parameters along with experimental methods and conditions, and structural, functional and literature information. The sequence and structural information of proteins is connected with thermodynamic data through links between entries in Protein Data Bank, Protein Information Resource and SWISS-PROT and the data in ProTherm. ProTherm now has a separated field for the Gibbs free energy change obtained at extrapolated temperature from the data on denaturation temperature measured by the thermal denaturation method. Both JPD and STING Report now offer link to ProTherm specific page and embedded parameter which indicates how many mutations exist in ProTherm DB for a given residue in a given PDB structure. In collaboration with Akinori Sarai's group, we have completely reorganized the table of indexes for easier identification of ProTherm entries on residue by residue basis (anchored to the specific PDB entry). |
| 7 | Ca/Ca- Cß/Cß Detailed and Global Insight ® | - |
Earlier version of the Ca/Ca- Cß/Cß Java Plot was not very practical if a user would like to examine the global plot of the protein with more than 100 amino acids. Current Diamond STING version of Ca/Ca- Cß/Cß Java Plot has both the global and detailed view easily generated and presented for analysis. |
| 8 | Adjustment for Color Range/Intensity in JPD ® | - |
Current version of JavaProtein Dossier permits adjustment of the color range for easier grasping of the differences among residues. The parameters might be now painted according to the numerical/color values spanning Min/Max range for the whole PDB, for the Protein family, for a given PDB structure and for specific parameter line. Although this feature does not influence the SELECT process, it does enhance the visual identification of amino acids having a different parameter value/color from the others within a same structure. |
| 9 | Extended SELECT in JPD ® | - |
Current DIAMOND STING SELECT feature is more powerful than the earlier as we added several enhancement options for the parameter range selection and Boolean logic combinations as well as by adding the new parameters to be selected from. |
| 10 | Local File by e-mail ® | - |
One of the main new features added to DIAMOND STING is the ability of the STING server to handle a user request for calculating all structure parameters for nonpublic (non PDB deposited) structure - a local file. As such requests are numerous and are CPU time demanding, it was very important to introduce a control of CPU use by placing all request in a job request list, executed by the order of arrival by 4 dedicated CPUs. |
| 11 |
Sting Report Expanded and now available for
a Whole Protein Chain Descriptors
® |
- |
Main addition in STING Report is that the DIAMOND version now
contains all new parameters (Order of CrossLink, Order of CrossPresence,
Space Clash, Rotamer Library ID, ProTherm ID) in addition to
the chain descriptors: |
GOLD Sting
was released in February 15, 2004
[ reference
]
GOLD Sting
was released in February 15, 2004
[ reference
]
| New features introduced in GOLD Sting: |
| # |
New Feature |
Gold Sting/ Sting
2.3 difference |
Description |
| 1 | Java Protein Dossier® | - |
Java Protein Dossier is a interactive presentation of important physical-chemical characteristics of the macromolecular structure described in a PDB file. With a few mouse clicks the user can access data about chosen parameter, call other Gold Sting modules or refine the search for a specific characteristics. By using color code scales for each residue of the sequence, JPD shows corresponding: temperature factor, solvent accessibility of the single chain (and also in complex with the other present chains in given PDB file), hydrophobicity, sequence conservation in a multiple alignment (relative entropy), double occupancy, reliability and histograms representing the atomic contacts. JPD also shows the identification of Interface Forming Residue (IFR) and their internal contacts. JPD offers information about electrostatic potential and curvature on protein surface. In addition, comparison of the Secondary Structure annotated by PDB, by DSSP and by Stride is presented. |
| 2 | Java Table of Contacts® | - |
Java Table of Contacts is a interactive tool for listing contacts between residues of one protein and dividing them in specific classes. JTC shows all contacts for a specified residue, IFR Contacts and also Protein-DNA Contacts. This interactive tool allows user to access other Gold Sting components or have physical-chemical parameters already "painted" within the table, such as: relative entropy, accessibility, secondary structure and the distance for the identified contacts. The user can make a choice of the residues important for his consideration, make them appropriately displayed and then print the table of publication quality. |
| 3 | Gold Sting Report® | - |
GOLD STING Report is a web based application for extracting concise and focused information from the GOLD STING Data Base on specific amino acids within the structures described in PDB files. The extracted information is presented to a user through a series of GIF images and a table of numerical values for the set of structure/function descriptors/parameters, generated by the GOLD STING components. The resulting HTML page with the GIF images and the table is ready to be printed and most importantly, it can be visualize at platforms with the most elementary configurations (no java, chime, plug-ins etc.). Below is a schematic view of GIF image panels which are generally produced by the GOLD STING Report. We have used 1cho.pdb, chain E, residue HIS_57 to generate GOLD STING Report for this help. Other panels will be added with the time, making GOLD STING Report GIF image collection more extensive. |
| 4 | ConSSeq | © |
The user now can ask ConSSeq to present logo produced by using MSA from both HSSP and our own HS2Qs. User can compare the logos as well as MSAs and Phylogenetic Tree through SeaView and TreeView packages, respectively. |
| 5 | Gold Sting MSA® |
- |
GS_MSA stands for the new Gold Sting component: Multiple Sequence Alignment. Those sequences are extracted both from HSSP and from our own SH2Qs (Sequences Homologue to the Query [Structure-having] Sequence). The latter one is designed so that we can benefit from the possibility of making a choice of the number of sequences that we want to consider in the relative entropy calculation. GS_MSA will use standard MSA viewer package: SeaView. |
| 6 | Gold Sting Phylogenetic Tree® | - |
GS_P3 sands for Gold Sting Phylogenetic Tree component. Phylogenetic tree is generated starting from either HSSP or SH2Qs multiple sequence alignments. TreeView standard viewer package is used to present to a user calculated phylogenetic trees. |
| 7 | Protein/DNA Contacts® |
- |
This Gold Sting component demonstrates relevant contacts being established across the interface formed by protein and DNA chain. Similar logistics is used here as in IFR Graphical Contacts. |
Sting version 2.3
was released in January 10, 2003
[ reference
(Bioinformatics) ] [
reference
(NAR) ]
| New features introduced in Sting version 2.3: |
| # |
New Feature |
Sting 2.2/2.3
difference |
Description |
| 1 | Free access to your local PDB format files | We have removed requirement for the user to register in order to get the permission to analyze his/her own PDB format files by Sting. This, we believe, will further facilitate the use of program and many requests for the registration waiver are since considered to be obsolete. | |
| 2 | Sting 2.3 Now available for LINUX ® | - |
As a major advance in spreading the use of our Sting is a possibility to use it on clients with LINUX operating system. We have tested some solutions and successful outcome will please ever growing community of colleagues using this OS. |
| 3 | ConSSeq | Significant improvements have been added to the Sting component: ConSSeq. This very important tool for accessing sequence conservation during evolution is now completely integrated with Sting sequence and structure frame, allowing for interactivity across those three windows. | |
| 4 | New Link: ProTherm ® |
- |
ProTherm is a collection of numerical data of thermodynamic parameters such as Gibbs free energy change, enthalpy change, heat capacity change, transition temperature etc. for wild type and mutant proteins, that are important for understanding the structure and stability of proteins. It also contains information about secondary structure and accessibility of wild type residues, experimental conditions (pH, temperature, buffer, ion and protein concentration), measurements and methods used for each data, and activity information (Km and Kcat ). |
| 5 | New mirrors sites ® | - |
Sting is now offered through
another 3 new mirror sites: |
Earlier, STING Millennium
version 2.2, was released on October 01, 2002
| New features introduced in Sting version 2.2: |
| # |
New Feature |
Sting 2.1/2.2
difference |
Description |
| 1 | Ca-Ca distances on Java plot ® | - |
Java Ca-Ca Distance Plot is a diagram where the distances between the alfa carbon of one residue and all alfa carbon atoms of other residues, within a single chain of the PDB file, are represented by colored squares in a symmetrical plot. |
| 2 | Cb-Cb distances on Java Plot ® | - |
Java CB-CB Distance Plot is a diagram where the distances between the beta carbon of one residue and all beta carbon atoms of other residues, within a single chain of the PDB file, are represented by colored squares in a symmetrical plot. |
| 3 | Contacts totally revised with better definitions ® |
Contacts have been revised so that we have now a complete list of all of possible contacts among any two amino acids within one chain or across the interface; this means that until Sting 2.1 we did register only the shortest of contacts (say among hydrophobic ones, or any other type) established among two amino acids. In Sting 2.2, Graphical Contacts, IFR Contacts and Protein Dossier do show all identified contacts. | |
| 4 | IFR Contacts redefined ® with adequate presentation in PD ® |
IFR contacts now includes also those residues that can make contact but do not belong to the INTERFACE! This is because Interface Forming Residues are strictly defined based on solvent accessibility. However, even those residues on the surface of facing chains that did NOT loose accessibility to the solvent, still can make for example HB, as the distance from donor to the acceptor is larger than the diameter of the water molecule used to define IFRs. See blue underlined residues (extended interface) in PD Interface (red underlined) [D_25 and N_29 in Chain 1]{in PD example under the pointer ® on the left!}. Note: as IFR Graphical Contacts does not have access to data on solvent accessibility, above mentioned residues are underlined in red as if they belong to the Interface ensemble strictu sensu! | |
| 5 | Aromatic stacking contacts included in Graphical
Contacts (GC), IFR Contacts (IFRC) and PD ® |
- |
Interaction among amino acids with aromatic ring are now identified and represented in GC, IFR_C and PD. See W_21 and aromatic stacking (gray line) with R_61 and F_79 {in example under the pointer ® on the left!} |
| 6 | Hydrogen Bonds now with up to
two intermediary water molecules included on GC, IFRC and Protein
Dossier (PD) ® |
Going through the literature and based on personal contacts with some of our collaborators, we extended the list of potential Hydrogen donors and acceptors, so total number of identified Hydrogen Bonds is now more extensive. This is explained in the Sting manual. Here , special attention is given to presence of water molecules that co-crystalized with the protein. See A_5 and its hydrogen bonds with intervening water molecules [represented as small balls on contact lines in GC presentation] {in example under the pointer ® on the left!} | |
| 7 | Stride Secondary Structure definition included on Protein Dossier (PD) ® | Secondary structure as calculated by STRIDE algorithm;
see: Frishman D, Argos P. Knowledge-based protein secondary structure assignment. Proteins. 1995 Dec;23(4):566-79. {this one is to complement already existing PDB definitions/annotations of Secondary structure and also DSSP definitions.} |
|
| 8 | Protein Dossier includes dihedral angles ® | We are now offering on PD indication of values for Phi and Psi angles for each amino acid, color coded with respect to allowed and disallowed areas in Ramachandran plot. | |
| 9 | Sting Java Ramachandran Plot includes statistical expectation for overall structure quality. ® | - |
Sting Java Ramachandran Plot includes now statistical expectation for number of amino acids with their Phi and Psi angles within allowed areas. |
| 10 | PDBMining revised and new features added ® | "PDB files sorted by # of identified Crystal H2O" and "PDB files sorted by # of identified Ligands" are now presented in a table with alphanumeric order of protein (type) with which H2O/Ligand is conne | |
| 11 | New links: ® |
- |
New links added:
SuperFamily, LPC, InterPro, ProtoMap, SMART, Pfam, CSU, DDD,
Expasy, BRENDA, Protein Mutant Database, KEGG, NCBI PubMed,
NCBI Protein Codes, NCBI Nucleotide Codes, NCBI PDB Codes, NCBI
3D Domains, NCBI OMIM, IUBMB Enzyme Nomenclature, WIT, EMP Project,
PDB Structure for EC number, Systers for EC number and Structural
Alignment at Yale |
| 12 | indexed help ® | - |
- |
| 13 | Completely new graphical solution for Sting entry web page ® | Sting 2.2 is now offering entry page which prompts the user to make a choice among 3 different WEB pages: A) Sting 2.1 extended page [including new Sting 2.2 features] which is specially tuned for slow Internet connection; B) Sting 2.2 reach graphical format page with artistic illustrations and C) Reach graphical format page with molecular images illustrations. |
| New features introduced in Sting version 2.1: 1. Definition of carefully selected Testing
Set of PDB files used to check all Sting features. |
- Earlier, STING
Millennium version 2.o, was released on September
01, 2001
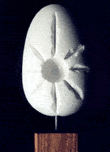
The image below shows all STING parameters available, encapsuled in
97 classes.
In chart below we show general outline of how Sting
is organized, executed and accessed, as well as the differences between
Sting version 1 (in blue) and the GOLD
Sting release = version 2 (in red). The elements of the Diamond
Sting version (#3) are in green color and the elements of the
Star Sting version (#4) are in black color.
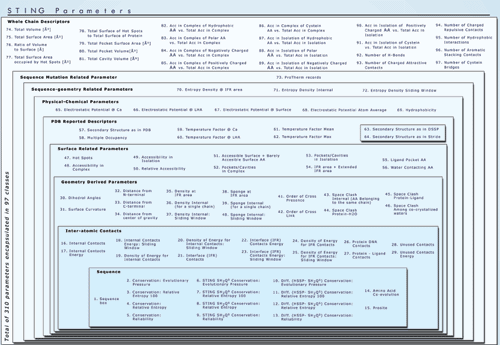
Above image represents the organization of older Sting version (SMS 2.0)
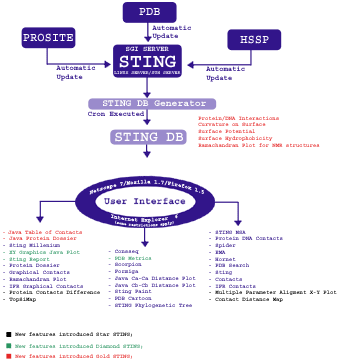
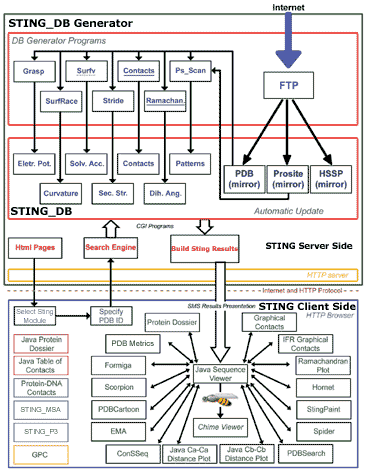
Above image is a schematic diagram illustrating the architecture of Sting. Sting is organized in two logical layers: Sting server and Sting client. On the server side, illustrated inside the large green box, are carried out all updates of the public domain databases used by Sting and the subsequent calculation of macromolecular properties. The Sting client side, illustrated inside the large blue box, provides a user friendly graphical interface and communicates to Sting server. The Sting versions 2.3, 3 and GOLD STING components are listed within black, red, blue and yellow border boxes, respectively.
 |
Work in progress: |
Table indicating current developments and future Sting releases
| Sting version |
New Sting features |
Release date |
|
| N/A |
1. Whole STING_DB will
be ported into relational DB |
February,
2007 |
|
| 2. Search for structures (across the entire PDB) satisfying a chosen range for set of structure/function parameters/descriptors | |||
| 3. Sting Report available in PDF format | |||
| 4. New
Parameters to be added: |
|||
| a). |
Moving Protein Parts | ||
| b). |
Preferred AA local environment in a given structure/family/whole PDB | ||
| c). |
Preferred AA
local contacts in a given structure/family/whole PDB |
||
 |
How to use PDB_Metrics |
On August 17 2001, PDB had:
See here how to get most updated values for these items as well as what other information {much more interesting} you may get by accessing PDB_Metrics.
29 files with no protein or DNA chain (just HETATOMS structure)
8000 PDB files with single chain structures (50.7% of total)
4433 PDB files with two chain structures ( 28.1% of total)
14946 PDB files contain structures with 5 or less chains (95% of total files).
 |
Data parsing and Links: |
We have compiled extensive list of links so that information about a same PDB file (and provided by other groups) can be easily accessed. See here list of LINKS and how to use them to their full potential.
 |
Known bugs and "very specific PDB files": |
| This software is under continuous development and we expect bugs to be found (not very eagerly tough). Please contact us if you find any problem! Please use PDB_Metrics extensively in order to understand better what are you looking at and whether you may get information you are expecting! |
| Sting is now fully compatible with Microsoft Internet Explorer and Netscape. As of now, you may use only Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.72 or Netscape versions lower than 6.0. See here more details on this subject! |
| At this moment, we do know that if you have
more than one browser opened with STING (or other CHIME
application), you may experience
some erratic behavior in terms of commands being executed on
a wrong destination (Chime window), but, good news is: not
always! So you may boldly go and venture
into multi-window analysis (looking at two or more structures
{PDB files}). |
- Some physics
and curios observations - courtesy of Sting:
- Interestingly and rarely (PDB files such as:1afa, 1rbd,
1a25, 1rbi, 2bpa, 1bk6, 1f8v, 1loc, 19gs), we observed
that HORNET will indicate Hydrogen Bonds bridging
two chains where either donor or acceptor would NOT be part
of IFR ensemble. By definition, this is not possible so we went
to great extents to find the source of the bug! However, we
found that this is a result (physically completely plausible)
of discrepancy that exist in algorithms used to calculate IFR
ensemble and Hydrogen Bonds. While the former one is defining
IFR after calculation of the LOST solvent accessible area, Hydrogen
bonds algorithm is using distance limits within which H-bond
is allowed to be formed. Consequently, one amino acid may not
lose any surface area accessible to the solvent prior to complex
formation (therefore it would NOT be a part of the IFR ensemble),
and yet it will be a part of the Hydrogen bond whose complement
belongs to the other chain. We remain Sting users that surface
accessibility is calculated based on rolling water molecule
with its van der Waals radius, while hydrogen bond maximal allowed
distance between acceptor and the donor is of 3.2 Å.
- Interestingly and rarely (PDB files such as:1afa, 1rbd,
1a25, 1rbi, 2bpa, 1bk6, 1f8v, 1loc, 19gs), we observed
that HORNET will indicate Hydrogen Bonds bridging
two chains where either donor or acceptor would NOT be part
of IFR ensemble. By definition, this is not possible so we went
to great extents to find the source of the bug! However, we
found that this is a result (physically completely plausible)
of discrepancy that exist in algorithms used to calculate IFR
ensemble and Hydrogen Bonds. While the former one is defining
IFR after calculation of the LOST solvent accessible area, Hydrogen
bonds algorithm is using distance limits within which H-bond
is allowed to be formed. Consequently, one amino acid may not
lose any surface area accessible to the solvent prior to complex
formation (therefore it would NOT be a part of the IFR ensemble),
and yet it will be a part of the Hydrogen bond whose complement
belongs to the other chain. We remain Sting users that surface
accessibility is calculated based on rolling water molecule
with its van der Waals radius, while hydrogen bond maximal allowed
distance between acceptor and the donor is of 3.2 Å.
- Important
REMAINDER:
- Ramachandran Plot will not produce any data for PDB files containing only DNA/RNA and/or HETATOM molecules!
- ConSSeq will not produce any data for PDB files containing only DNA/RNA and/or HETATOM molecules!
- SCORPION will not produce any data for chains containing only DNA/RNA and/or HETATOM molecules!
- Graphical Contacts will not produce any data for PDB files containing only DNA/RNA and/or HETATOM molecules!
- HORNET will not function properly if one of the chains indicated to make hydrogen bonds is DNA/RNA (ex: 1c0a.pdb)
- FORMIGA will not produce data for chains containing DNA/RNA (ex: 1f8v.pdb)
- Sting option from Windows menu: Neighbors, will not operate on DNA/RNA
- Pockets will not produce data for protein structures
that are missing some of the backbone atoms! We have found around
100 PDB files that belong to this category.
- It is Not a BUG!:
STING DataBase updating and renewal Resulting effect STING_DB update = weekly updates in synchrony with the PDB updates All parameters calculated for newly added PDB files (duration: approximately 8 hours for weekly added 120 PDB files, on 4 R14000 500MhZ SGI CPUs) STING_DB renewal = bimonthly activity undertaken to synchronize variety of parameters (mainly linked to residue conservation) to the data in HSSP and SwissProt. Parameters related to conservation (HSSP/SH2Qs) relative entropy, MSA, Evolutionary pressure are all recalculated based on both HSSP and SwissProt latest release.(duration: approximately24 days using 32 CPUs on our linux Cluster [Pentium 1Ghz]) plus 4 R14000 500MhZ SGI CPUs +2 Xeon 3.2 Ghz CPUs)
- Issues related to synchronization of the STING (JPD) Database with the public database updates
- Incomplete data
- The STING DB is regularly updated in synchrony with the PDB
updates. This happens once a week. All the parameters for new
PDB entries are calculated by our server. However, some items
will be missing. Namely, The HSSP related parameters will be
missing. They will be added once the STING DB generator identifies
that the new HSSP is offering until that moment a not present
PDB entry.
In addiction, with any new HSSP version and new SwissProt version, all data on conservation has to be calculated. As this requires an enormous load on our CPUs, the STING DB renewal is done every two months.
- When a new PDB file is deposited at the RCSB/PDB, STING_DB_Generator
(STING DataBase Generator) will make necessary updates in STING_DB.
The STING_DB is consulted by the JavaProtein Dossier
and ConSSeq to show a variety of data. However, if the corresponding
HSSP file is not generated
yet (usually, the HSSP will
make available corresponding new entry at least 2 weeks after
the PDB release date), our STING_DB will be incomplete. Consequently,
the JavaProtein Dossier
and ConSSeq
will show no data that are drown or calculated from data made
available by the HSSP. This
"delay time" is usually measured in couple
of weeks or more. If you are eager to see the complete STING/JPD
data for a new structure, check back with us in about 2 weeks.
It is likely that the complete data will be there.
- If you have incomplete JavaProtein Dossier information,
before jumping into a conclusion that you found a new GS bug,
verify if a given "incompleteness" is due to the fact
that a PDB file describes multiple copies of a given monomer.
Such case is easily verified in 1a12.pdb (guanine nucleotide
exchange factor) where 3 copies of the same monomer are described.
JavaProtein Dossier
will paint all parameters only for the chain A and not for the
chains B and C. However, the missing parameters are exactly
the same for all 3 chains. Similar situation is found for 9xin.pdb;
here we have 4 copies of the same monomer, but only the first
chain (the A chain) has a complete list of the Protein Dossier
Parameters. Note: in this cases watch also for the apparently
confusing IFR contacts: they appear to be mirroring same contacts,
but they are real and reflect contacts among copies of monomers!
- Protein Dossier will have a problem to show complete
set of data for 1gav.pdb. This particular PDB
file contains information about 45 chains. {See here
for other PDB files containing large number of chains!}.Generated
image with all structure/function descriptors is so large, so
that browser will not be able to show it. However, there will
be an icon shown by browser. Click on this icon and then save
the image on your local computer. Next, you may open that image
by any image editor pogrom and by doing so, see a complete Protein
Dossier information.
- Protein Dossier is not always able to identify pattern indicated
by PROSITE in the sequence under analysis. However, PROSITE
pattern identifier will be present on the graphical preamble
of Protein Dossier. We have identified couple of cases: 1a2u.pdb
and 101m.pdb. The user is invited to analyze in details
PROSITE given pattern and see why our algorithm is not able
to decipher the position of this pattern within the sequence
being analyzed.
- Protein Dossier may show apparently curios data, however,
we always recommend that the user checks out parameter values
before deciding that a new bug was found; Here is one interesting
example: 1a6x.pdb contains in PDB file under
temperature factor column, only value of 1 for all atoms. Consequently,
Protein Dossier will show empty line for temperature factor.
Without knowing TF value, the user might be inclined to think
that PD is not operating well at this particular point.
- Also, we have noticed that very creative residue
numbering in PDB files can cause sequence
window to halt. We found couple of examples: 1bmv.pdb
and 135d.pdb; if you find more, please contact
us. {The latter PDB file has following residue numbering:1-7;1L;5L;8-14;6L;10L;15-21
?!?!?!}. Such PDB files will also cause problems on other Sting
components (including those components that are invoked directly
by some other external Sting server).
- THIS is now SOLVED! We continue to
show description of the problem that existed earlier with the
intention to catalogue all specific problems and consequently,
specificity of the PDB! (STING Millennium will not
show sequence for PDB files that have more than one chain and
at least one of those does NOT have chain identifier. Example
for this one is: 1rbc.pdb). See here
most recent data on all PDB files containing chains with NO
IDentifier!This is SOLVED!!
- PDB files as above described 1rbc.pdb (see here
most recent data on all PDB files with more than one chain and
containing at least one chain with NO Identifier) might introduce
unexpected behavior in some of the Sting components. This is
mainly due to the fact that CHIME and CHIME scripts do not handle
properly chains with no Identifier However, there are only about
20 of these files as of September 1st 2001.
- Sometimes you'll notice that Gold Sting Sequence Frame starts
with the List Box for choosing Rendering Style (right side of
the icon <?>) too small. This seems to be a bug of Java
Virtual Machine. Usually, if you change the dimensions of the
Sequence Frame the List Box gets its usual dimensions.
- If the protein you're interested on has chain IDs in the range
0-9, be aware that Chime Plug-in doesn't work properly in this
case. Functions like Windows/Surface and Int Surface/Interface
Component/Charges on Interface may present unexpected results.
This is the case of 2bpa.pdb.
- Very Specific PDB Files are those that have
only HETATOMs and NO protein or DNA chain. They will
show up on STING's graphics window, but will not have
anything to be shown on Sting's sequence window. See
for example PDB files: 1a7y.pdb, 1a7z.pdb, 1aa5.pdb, 1aga.pdb,
1ao2.pdb, 1ao4.pdb, 1c0q.pdb, 1c0r.pdb, 1c4s.pdb, 1c58.pdb,
1cap.pdb, 1car.pdb, 1dey.pdb, 1fvm.pdb, 1ghg.pdb, 1hpn.pdb,
1hua.pdb, 1hya.pdb, 1kes.pdb, 1pbl.pdb, 1pup.pdb, 1qd8.pdb,
1sho.pdb, 1tnl.pdb, 2c4s.pdb, 2hya.pdb, 3hya.pdb, 4hya.pdb and
9lyz.pdb. Those 29 files are the ones we identified
in PDB until August 06, 2001. In this case, we are reporting
"very specific PDB files", rather than STING problem!
See here
most recent data on all PDB files containing NOT even a single
chain identified!
- Ligand Pocket: THIS
is now SOLVED! We continue to show description of the problem
that existed earlier with the intention to catalogue all specific
problems and consequently, specificity of the PDB!
this option is found on Sequence Window/Action/Ligand/Ligand
Pocket! It does have a problem when the user makes an option
to click on REFRESH button, and then proceeds to see Ligand
Pocket for the PDB files that do have metals as HETATOMS =>
single metal atoms are not visible and LIGAND POCKET script
will "paint in thick wireframe" the pocket around
"INVISIBLE" (but present) metal atom; Take for example
1a65.pdb; There are 4 Cu atoms. LIGAND POCKET
script will paint pocket around those Cu atoms, but Cu atoms
themselves are invisible. In general, when that happens, the
best way to proceed is to use Sequence Frame/Windows/Send
Script option and issue following command: select
Cu or Mg or Ca or Cl or Fe or Mn or Br or Zn or Na; cpk;
______This will make those metal atoms visible! In case
of 1a65.pdb, for example, the user can consult PDB TXT file
menu option on Sequence Window/MODULES, and identify
which metal atom is present. As the user confirms presence of
Cu atoms, command to use in Sequence Frame/Windows/Send Script
would be: select Cu; cpk;___Consequently,
Cu atoms will be painted in CPK!This
is SOLVED!!
REAL BUGS:
- The STING DB is regularly updated in synchrony with the PDB
updates. This happens once a week. All the parameters for new
PDB entries are calculated by our server. However, some items
will be missing. Namely, The HSSP related parameters will be
missing. They will be added once the STING DB generator identifies
that the new HSSP is offering until that moment a not present
PDB entry.
- HORNET
- we found inconsistent response for PDB file: 2bpa.pdb
- curios IFR indicator is placed on GAP position #1 in PDB file: 1a28.pdb
- indicators of the secondary structure (underlined sequence: red=helix, blue=strand) is not consistent when order of chains requested to be analyzed does not follow order of their appearance in the PDB file. For example, there are 3 chains (A,B and C) ant those three appear in this exact order in the PDB file.; However, the user is requesting that interface is formed among chain C and chains A+B. Solution to this problem would be to follow order of appearance of the chains in the PDB file: A+B against C chain!
- SCORPION
- Requesting to see combined statistics of residue occurrence for multiple chains where at least one of them is without chain ID, the title in the resulting tale will not reflect presence of the chain without the ID. for example, in case of 2pad.pdb there are two chains and one is without ID. Marking both of them to be displayed will result in correct data presentation, but the title will state: "single chain"!
- The java applets used by SCORPION to present Residue Frequency has an incompatibility with Netscape 6/7 running java plug-in 1.3.1. Sometimes it gets stuck and that requires closed all Netscape's windows. This also happens to module FORMIGA. However, these applets work perfectly under Internet Explorer and Mozzila.
- CHIME limits; problems related here are caused by limits
that CHIME imposes on Sting. Number of functions will operate erratically
if one of the chains has no ID.
- Sting options from Windows menu : View Chain, Neighbors, Chain Color and Surface might operate erratically if one of the chains in the PDB file has no ID and that particular chain was included in the choice madden by the user.
- Sting options from Windows menu : Surface will not operate correctly with the PDB file contains chains with ID's which are numerical values rather than letters. Ex: 1afa.pdb.
- Sting options from Windows menu : Surface and its option Electrostatic Potential (E.P.) or Hydrophobicity (Hyd) would not operate always on CHIME. See example for chain B in 11ba.pdb and 1rbd.pdb.
- Sting options from Windows menu : Surface and its option Electrostatic Potential (EP) or Hydrophobicity (Hyd) would operate extremely slow (Sting window looks as it did hung up) on NMR/Model PDB files such as 1a57.pdb.
- Sting options from Surface menu : Show Interface, is not operating as was planed. We are working to eliminate this error.
- Chime does not handle properly PDB file: 2mrt.pdb -> Simple
rotation caused by mouse movement, will do rotation + random
translation of the molecule. It is not clear to us why this
happens.
 |
External LINKS to Sting and its components: |
Last Update: January 24, 2011
To make a link to Sting or any of its components,
having defined a PDB identifier (in this case we are going
to use PDB file 1ppf.pdb),
and also having defined the closest and most responsive Sting server
among our mirror sites, (in this example, we used URL of our home
site: http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br,
however, one can use one of our mirror sites: 1) at Columbia University
in New York - USA: http://trantor.bioc.columbia.edu,
or at 2) CNB in Madrid - Spain: http://www.es.embnet.org,
or at 3) Kyushu Institute of Technology - Fukuoka - Japan: http://gibk26.bse.kyutech.ac.jp, (historical mirrors, not working anymore: 4) RCSB/PDB in San Diego - USA: http://mirrors.rcsb.org,
5) AR.EMBnet - in La Plata - Argentina: http://www.ar.embnet.org, 6) Embrapa in Brasília - Brazil: http://asparagin.cenargen.embrapa.br)),
use following calls : ________________(see Note#1
and Note#2 below, for more details)
External link to STING Millennium:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?1ppf
External link to STAR Sting Report:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/smsReport/smsReport.pl?1ppf,E,195
http://sms.
cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/smsReport/smsReport.pl?1ppf,E
External Link to Ramachandran Plot:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?moduleOpen=Ramachandran&1ppf
External Link to Ramachandran Plot - Image:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/ramachandran/ramachandran.pl?pdp=1ppf
External Link to ConSSeq (requires chain identifier):
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?moduleOpen=ConSSeq:E&1ppf
External Link to HORNET:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/HORNET/verifica.pl?dir=pdb&pdb=1ppf
External Link to SCORPION (requires chain identifier):
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/SCORPION/monta_tela.pl?1ppf+E
External Link to FORMIGA (requires chain
identifiers for interface formation):
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/FORMIGA/formiga.pl?pdb_list=1ppf+E+I
and call only for the FORMIGA's table showing Lost Solvent Accessible
Area of IFRs:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/FORMIGA/formiga.pl?pdb_list=1ppf+E+I&option=html
External Link to Graphical Contacts:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?1ppf&moduleOpen=GraphicalContacts:E
External Link to IFR_Graphical Contacts:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?1ppf&moduleOpen=IFRContacts:I:E
External Link to STINGPaint:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/STINGpaint/STINGp.pl?PDB=true&pdbname=1ppf
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/STINGpaint/STINGp.pl?PDB=true&padrao=1&pdbname=1ppf
External Link to PDB_Cartoon:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/pdbcartoon/pdb_cartoon.pl?pdb=1ppf
External Link to Protein Dossier:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?moduleOpen=ProteinDossier&1ppf
External Link to Protein Dossier - Image:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/proteindossier/pd.pl?1ppf
External Link to STING_TGZ:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/download_tgz/download_tgz.pl?1ppf
External Link to Multiple Structure - Single Parameter
(MSSP) 2D plot:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?moduleOpen=MPA&1ppf
External Link to STING_DB QA:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/SMS/sting_db_qa/index.php
External Link to Contact Distance Map:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?moduleOpen=contactMap&1ppf
External Link to Protein Contacts Difference:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/pcd/pcd.pl?1ppfE;1ppfI;0
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/pcd/pcd.pl?1ppfE;1ppfI;1;95
External Link to TopSiMap:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/openJPD/openTopSiMap.pl?1ppfE;1sluB
Note#1: All Java applets: Ramachandran
Plot, Graphical Contacts and IFR Contacts and ConSSeq will open also
STING Millennium Graphics Window
and Sequence Window. This is because
those applets interact with 3D presentation (except ConSSeq) and it
is necessary to have both Graphics and Sequence Window opened. On
the other hand, Scorpion, Formiga, STINGPaint, PDB_Cartoon and Protein
Dossier do not need to open neither of those two windows. However,
we are now working on standardizing external call response so that
ALL components open also STING Millennium Graphics
Window and Sequence Window (mainly
to provide standardize response, but also to make possible access
to the HELP pages for the user that gets into these components by
the way of external calls made by other servers/products).
Historical archive (not needed anymore):
Note#2: when calls are forwarded
in order to show one of PDB files containing chains with no Identifier
(see above), then chain Identifier (for example:
"S") in ConSSeq call for 1rbc.pdb
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?moduleOpen=ConSSeq:S&1rbc
should be replaced with empty space:
http://sms.cbi.cnptia.embrapa.br/cgi-bin/SMS/STINGm/frame_java.pl?moduleOpen=ConSSeq:
&1rbc
8 steps for integrating a new module into STING
In order to integrate a new module into the STING suite, we need to make sure that the following 8 steps are all successfully completed:
| 1 | Develop the algorithm for a parameter/descriptor calculation and generate such data for a whole PDB. Include the new parameter into the STING_DB |
| 2 | Develop the adequate interface for demonstrating the data in a plausible way. |
| 3 | Write appropriate HELP pages for a new module with the illustrative figures and the snapshots of the screen output. |
| 4 | Include newly calculated parameter into the JPD graphical presentation and include this parameter into the SELECT interactive window |
| 5 | Provide for the procedure that would generate the IMAGE of the typical output for indicated PDB file, indicated chain and indicated amino acid (to be included into the STING REPORT). |
| 6 | Enable the URL indicator for the external direct calls to the module genereating the output for indicated PDB file, indicated chain and indicated Amino Acid. |
| 7 | Include the algorithm for a new parameter calculation into a procedure that calculates all STING parameters for newly deposited PDB files (weekly update) and if applicable, to a procedure which re-calculates those parameters (such as: conservation, co-evolution) which are dependent on a content of other databases (such as SwissProt/TrEMBL) - usually performed on a bi monthly basis. Also, the algorithm should be implemented for the calculation of local file aprameters: the STING TGZ file. |
| 8 | Make exhaustive tests using carefully selected PDB files chosen to represent most diversified structure content, in order to make sure that the module would function for the most structures. |
 |
Testing set of PDB files used to check all Star STING features : |
Last Update: January 24, 2011
Note: here is how we have chosen files listed
in the table below:
1. Six files with only ONE PROTEIN chain obtained by X-ray crystallography:
16vp,1 a54, 1 a65,1 a7g, 1akb,1akc
2. Three files with ONE Protein chain obtained by NMR: 1ay3,
1b3c, 1b9r
3. SIX files with only ONE PROTEIN chain obtained by X-ray crystallography
with chain ID:101m,102l, 107l,107m, 112l,112m
4. Three files with only ONE PROTEIN chain obtained by NMR with
chain ID: 1 a57, 1 a6x, 1adr
5. Six files with only ONE DNA chain, obtained by X-ray with chain
ID: 152d, 231d, 1c2x, 135d, 1ajf, 1kaj
6. Twelve files with TWO Protein chains obtained by X-ray crystallography:11ba,14gs,
15c8,19gs, 1a25,1 a28, 1pad,1rbd, 1rbh,2pad,
1rbi,3cpa
7. Three files with TWO chains but one chain is DNA (x-ray or NMR):
1 akx, 1c0a
8. ONE to Three files with two chains where at least one chain has
non-amino acids or incomplete Amino acids in the chain: 148l
9. Six files with THREE chains X-ray with chain ID:1
a0t, 1 a3e, 1 afa, 1bmv, 4cpa
10. Three files with Three chains one of which is DNA: NO such file
in PDB!
11. Four files with FOUR chains: X-ray: 1 a6z,
1 a1r, 1 a4w, 2bpa
12. One file with Five chains: 1 ar9
13. One file with SIX chains: 1bk6
14. One File with SEVEN chains: 1f8v
15. One file with TWELVE chains: 1loc
16. One file with TWENTY TWO chains: 1bgy
Table of PDB files used to check all Star STING components
PDB file |
Number of chains in PDB file |
Proteic chain ID |
DNA/RNA chain ID |
List of all chain Id's present in PDB file |
Model (NMR)with # of models |
|
16vp |
1 |
A |
|
A |
- |
|
1a54 |
1 |
A |
|
A |
- |
|
1a65 |
1 |
A |
|
A |
- |
|
1a7g |
1 |
E |
|
E |
- |
|
1akb |
1 |
A |
|
A |
- |
|
1akc |
1 |
A |
|
A |
- |
|
1ay3 |
1 |
A |
|
A |
27 |
|
1b3c |
1 |
A |
|
A |
40 |
|
1b9r |
1 |
A |
A |
15 |
|
|
101m |
1 |
A |
A |
- |
|
|
102l |
1 |
A | A |
- |
|
|
107l |
1 |
A | A |
- |
|
|
107m |
1 |
A |
A |
- |
|
|
112l |
1 |
A | A |
- |
|
|
112m |
1 |
A | A |
- |
|
|
1a57 |
1 |
A | A |
20 |
|
|
1a6x |
1 |
A | A |
49 |
|
|
1adr |
1 |
A | A |
20 |
|
|
152d |
1 |
A |
A |
- |
|
|
231d |
1 |
A |
A |
- |
|
|
1c2x |
1 |
C |
C |
- |
|
|
135d |
1 |
A | A |
- |
|
|
1ajf |
1 |
A | A |
- |
|
|
1kaj |
1 |
A | A |
- |
|
|
11ba |
2 |
A,B |
A,B |
- |
|
|
14gs |
2 |
A,B |
A,B |
- |
|
|
15c8 |
2 |
L,H |
L,H |
- |
|
|
19gs |
2 |
A,B |
A,B |
- |
|
|
1a25 |
2 |
A,B |
A,B |
- |
|
|
1a28 |
2 |
A,B |
A,B |
- |
|
|
1pad |
2 |
A,I | A,I |
- |
|
|
1rbd |
2 |
S,A |
S,A |
- |
|
|
1rbh |
2 |
S,A |
S,A |
- |
|
|
2pad |
2 |
A | A |
- |
|
|
1rbi |
2 |
S,A |
S,A |
- |
|
|
3cpa |
2 |
A,S | A,S |
- |
|
|
1akx |
2 |
B |
A |
A,B |
- |
|
1c0a |
2 |
A |
B |
A,B |
- |
|
148l |
2 |
E,S |
E,S |
- |
|
|
1a0t |
3 |
P,Q,R |
P,Q,R |
- |
|
|
1a3e |
3 |
L,H,I |
L,H,I |
- |
|
|
1afa |
3 |
1,2,3 |
1,2,3 |
- |
|
|
1bmv |
3 |
1,2 |
1,2 |
- |
|
|
4cpa |
3 |
A,I,B,J | A,I,B,J |
- |
|
|
1a6z |
4 |
A,B,C,D |
A,B,C,D |
- |
|
|
1a1r |
4 |
A,B,C,D |
A,B,C,D |
- |
|
|
1a4w |
4 |
L,H,I,R |
L,H,I,R |
- |
|
|
2bpa |
4 |
1,2,3,A |
1,2,3,A |
- |
|
|
1ar9 |
5 |
0,1,2,3,4 |
0,1,2,3,4 |
- |
|
|
1bk6 |
6 |
A,C,D,B,E,F |
A,C,D,B,E,F |
- |
|
|
1f8v |
7 |
A,D,B,E,C,F |
R |
R,A,D,B,E,C,F |
- |
|
1loc |
12 |
A,B,1,C,D, 2,E,F,3,G, H,4 |
A,B,1,C,D, 2,E,F,3,G, H,4 |
- |
|
|
1bgy |
22 |
A,B,C,D,E, F,G,H,I,J, K,M,N,O,P, Q,R,S,T,U, V,W |
A,B,C,D,E, F,G,H,I,J, K,M,N,O,P, Q,R,S,T,U, V,W |
- |