Conservation of sequence according to STING´s SH2QS
The Amino acid sequence conservation and reliability according to SH2Qs data is shown here. The Evolutionary Pressure, calculated based on SH2Qs alignments (adequately prepared by BLUE STAR STING) to be served as an input to Rate4Site (8) software, is also presented.
Note:
for some short protein peptide structures (see for such example in 1rbd.pdb)
the SH2Qs does not encounter any similar and yet "significant"
sequences in order to calculate reliable conservation parameters.
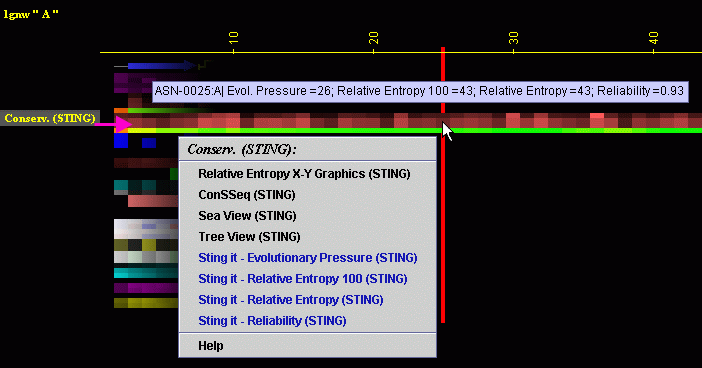
Placing the cursor above this element: pop-up area will show the position
(sequence number and amino acid three letter code) for selected amino
acid and the 4 numerical values for Conservation for given amino acid.
Left mouse click: no action
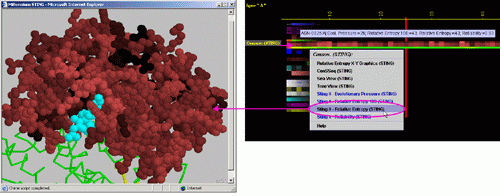
Right mouse
click: on any of the "Conserv.(SH2Qs)"
will generate following menu and actions:
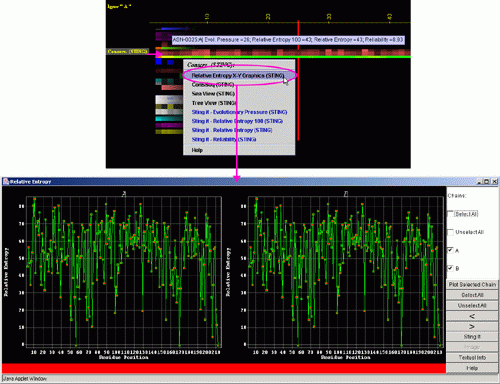
A) "Temperature
Factor X-Y Graphics" will produce following Java X-Y graphics (X=
sequence number, Y= Relative Entropy) with the interactive possibilities
described in dedicated
HELP manual:
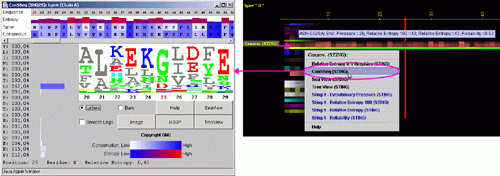
B) ConSSeq: This option invokes a ConSSeq component of BLUE STAR STING with
its characteristic display. See more details about ConSSeq in its own
help
pages.
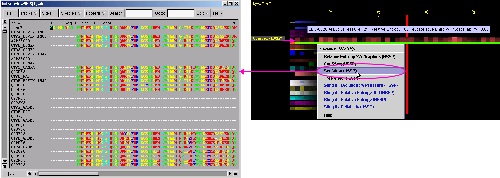
C) SeaView Multiple
Sequence Alignment editor will show all the sequences used by SH2Qs
in order to calculate consensus sequence and relative entropy.
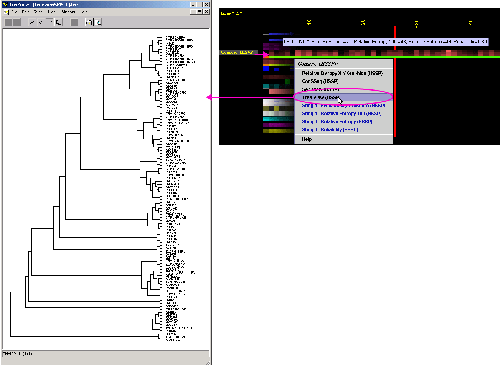
D) TreeView Phylogenetic
tree viewer will show all the relationship of sequences aligned and used
by SH2Qs
in order to calculate consensus sequence and relative entropy. Tree is
calculated using ClustalW software. The input to ClustalW was the BLUE STAR
STING especially prepared MSA, based on SH2Qs.
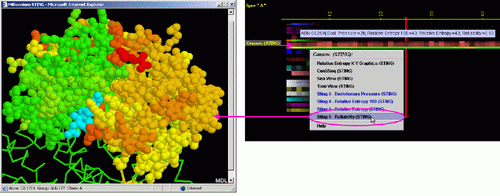
E) STING it "Evolutionary
Pressure (SH2Qs)":
This option generates structural presentation with color coding of the
amino acids corresponding to the JPD color coding for this particular
parameter. Amino acids are presented in CPK rendering. This feature is
exceptionally useful as it allows to a user to inspect within the structure,
a parameter describing a sequence conservation.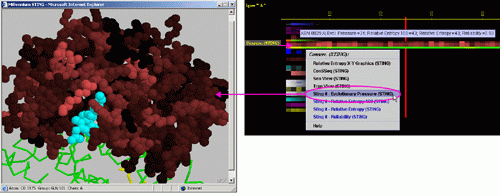
F) STING it "Reliability":
This option generates structural presentation with color coding of the
amino acids corresponding to the JPD color coding for this particular
parameter. Amino acids are presented in CPK rendering. This feature is
necessary if a user wishes to evaluate the reliability of the calculated
conservation parameter. If all sequences used for the MSA are present
at this particular position in the sequence, then the reliability is equal
to 1 (100). If say only 15 sequences are showing an amino acid at this
particular position in the sequence, while SH2Qs
have collected 100 sequences in total, then the reliability is equal to
0.15(15). For cases where only up to 5 sequences were identified by the
SH2Qs
for calculation of the relative entropy, we decided to attribute value
of ZERO for the reliability.
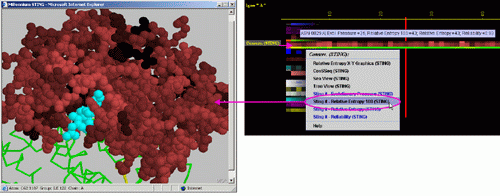
G) STING it "Relative
Entropy (SH2Qs)":
This option generates structural presentation with color coding of the
amino acids corresponding to the JPD color coding for this particular
parameter. Amino acids are presented in CPK rendering. This feature is
exceptionally useful as it allows to a user to inspect within the structure,
a parameter describing a sequence conservation.
H) STING it "Reliability": This option generates structural
presentation with color coding of the amino acids corresponding to the
JPD color coding for this particular parameter. Amino acids are presented
in CPK rendering. This feature is necessary if a user wishes to evaluate
the reliability of the calculated conservation parameter. If all sequences
used for the MSA are present at this particular position in the sequence,
then the reliability is equal to 1 (100). If say only 15 sequences are
showing an amino acid at this particular position in the sequence, while
SH2Qs
have collected 100 sequences in total, then the reliability is equal to
0.15(15). For cases where only up to 5 sequences were identified by the
HSSP for calculation of the relative entropy, we decided to attribute
value of ZERO for the reliability.